The basic idea behind asset allocation is to create a diversified portfolio so that one set of investments in an asset class will rise or fall at different times than others in the portfolio during a market cycle.
While counterintuitive, sometimes adding a risky asset to a portfolio can reduce its overall risk. This can be considered a form of hedging. Adding groups of riskier assets than the core portfolio requires some advanced asset allocation decisions. These decisions can be better made once an investor knows their portfolio’s risks.
Types of Risk
While investors acknowledge the idea of risk, many people don’t know how many types of risk can affect their portfolio. At any one time, a portfolio faces:
- Principal risk: the chance you have invested money will decline in value.
- Credit risk: the chance a borrower will default on an obligation.
- Market risk is the likelihood that a broad investment market, such as the bond or stock market, will decline in value.
- Liquidity risk is the possibility that you won’t be able to sell or convert a security into cash when needed.
When the sources of portfolio risk are independent and the portfolio is diversified through the asset allocation process, exposure to any one risk source should be reduced. However, even in a diversified portfolio, market risk is present, which is the source of systemic or market-wide risk that cannot be diversified away.
Diversification, however, is not free. It can be considered a type of hedging strategy accompanied by a cost in the form of some assets designed to act as a counterweight to advancing assets. In any diversified portfolio, some assets will gain in price while others decrease. This is the trade-off in the risk-managed portfolio, but over time, the overall portfolio’s gains will outpace declines.
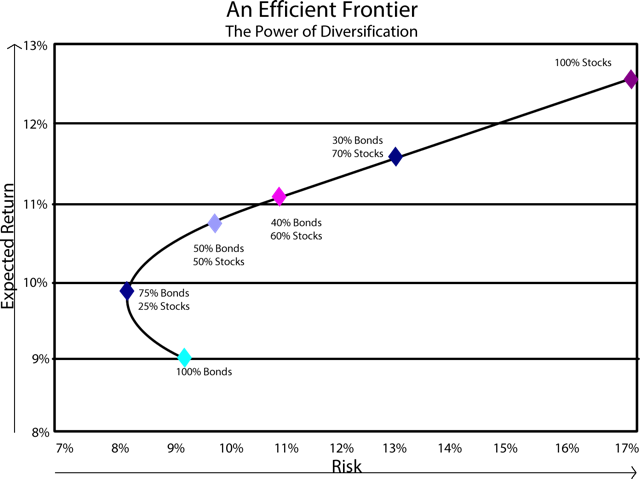
Advanced asset allocation relies on ideas from Modern Portfolio Theory. This theory, developed in the early 1950s by the legendary investment theoretician Harry Markowitz, uses statistical analysis to prove that the overall risk in any investment portfolio can be identified and managed by examining the risk relationships between combinations of investments.

An essential part of this theory is that risk can be managed through diversification and that a better risk-adjusted performing portfolio can be built using combinations of different assets.
This idea became so crucial that one landmark study found that asset allocation policy is so vital that it determines over 90% of a portfolio’s performance variability over time.
Types of Advanced Asset Allocation The basic idea of asset allocation is well-accepted today. Target-date funds and other professionally managed diversified portfolios are available as ETFs and mutual fund managers. They come in various risk levels and include various underlying asset classes. Investment managers use three main types of strategies to manage diversified portfolios. The plan mainly differs in terms of their time frames in response to market changes and their level of active management. Here are three main types of advanced allocation strategies:
Tactical Asset Allocation (TAA) is a strategy that adjusts portfolios in response to short-term changes in the markets or to pursue an investment opportunity, such as a rotation from small- to large-cap stocks or a downturn in international markets. TAA can also be used to adjust overall exposure in the pre-determined asset allocations that may have increased or decreased over time to bring them more in line with the owner’s risk tolerance. This is the idea behind Target Date Funds.
Strategic Asset Allocation
This strategy makes portfolio changes based on a longer time frame. It has a more passive management approach and requires less trading.
Dynamic Asset Allocation
This is the most active form of trading and is used to re-allocate a portfolio due to changing market conditions as they present themselves. This requires frequent trading and rebalancing and is the most expensive asset allocation trading strategy.
Core-Satellite Models
While the three asset allocation strategies listed above cover the level and frequency of trading and the need for active management, they still require a portfolio. This is where a core-satellite portfolio comes into the picture.
To meet an investor’s needs, a core-satellite strategy uses a core portfolio holding complemented by satellite positions, often in other mutual funds or ETFs.
This flexible strategy can meet the needs of investors with a range of risk tolerances. For example, investors with a higher risk tolerance can combine a growth portfolio with specialty mutual funds, ETFs, or alternative investments to increase the potential for total return.
A balanced portfolio can be combined with specialized equity or income-generating mutual funds or ETFs for investors with moderate risk tolerance. The goal is to provide the potential for capital appreciation and current income.
Tax-sensitive clients can use balanced or conservative growth portfolios with laddered municipal bonds or tax-exempt mutual funds to provide the potential for federal tax-exempt income with less risk.
Each core-satellite strategy can be supplemented with satellite positions in various asset classes. For instance, investors with higher risk tolerances can select ETFs in high-return market sectors and then sell those positions as that sector closes without disrupting the overall asset allocation strategy. The emphasis should be on managing the core portfolio and rebalancing to keep the overall asset class exposures and risk levels in line with the original investment goal.
Rebalancing is critical to any advanced allocation strategy in this strategy and others due to “drift” or “overlap.” This problem can be expensive and increase the risk to any allocation strategy, including the core-satellite approach.
The main reason is the product overlap between ETFs and mutual funds. By definition, ETFs are indexes comprised of different weightings in underlying stocks in a specific sector. When ETFs are combined with mutual funds, investors may find that despite the different products, they hold many of the same stocks.
Style drift can be problematic for investors concerned about having specific fund investment-style percentages within certain asset classes. For instance, if your target diversification for small-cap funds is 10% and your small-cap fund grows into the mid-cap category, your fund diversification will fall below 10%.
Investors can review the holding of funds quarterly, but ETF indexes and their respective holdings are rebalanced less frequently, usually annually. ETF rebalancing is a risk management tool, not a performance enhancer. However, investors managing their portfolios should rebalance in response to changing market conditions and underlying fund asset holdings.
Expanding the Asset Class Universe
Advanced asset allocation uses different management strategies along a spectrum of active and passive management. However, its portfolio composition also includes a much wider variety of other mutual funds and asset classes (equity, bond, alternatives).
Other asset classes or funds that can be added to the advanced diversification mix are high-yield funds, growth and income funds, growth funds, convertible securities, equity income funds, specialized equity ETFs and funds (technology, real estate, energy, ESG), and varieties of mid-, small-, and large-cap growth and value funds.
Fixed income is also part of this mix, including investment-grade corporates, governments, mortgage and asset-backed bonds, and high-yield bonds. The bonds can have various credit ratings and maturities.
Crypto is Not An Asset Class
Despite popular belief, cryptocurrencies in all forms, including tokens, are not an asset class and have no role in a serious investor’s portfolio. Crypto is a bet on price direction that is fueled by popular hype. Crypto does not pay a dividend, has no investment fundamentals, and has no characteristics that would be included in traditional fundamental analysis. Instead, crypto is used for tax evasion and money laundering, to destabilize central banks, and to fuel the online gambling industry. Crypto is as much of an asset class as horseracing, except that a horse race lasts a few minutes. However, it has more fundamentals to analyze, and crypto can be held for years. Those are the only differences. Crypto is not used anywhere in the world to replace a nation’s existing currency. Bottom line: don’t buy crypto.
The Role of Leveraged ETFs
One of the newest additions to the ETF world is leveraged ETFs. Some ETF firms offer these and allow investors to magnify price moves in any ETF by up to three times the daily price movement. Leveraged ETFs carry more risk, require more supervision, and should be used by more sophisticated investors. However, they present easy market access to capitalize on short-term market opportunities and may have a role in a core-satellite strategy.
Advanced Allocation Can Reduce Risk
Thanks to Modern Portfolio Theory, several different mutual and managed funds today can deliver a diversified portfolio of investments in a single fund. The top-rated target-date funds are an excellent example of a diversified portfolio that adjusts risk levels as the investor approaches retirement and their portfolio becomes more conservative. Combining asset classes is essential in any advanced asset allocation strategy. How many funds and ETFs are selected depends on the investor’s risk level, time frame, and portfolio size.
Modern Portfolio Theory is over 50 years old, but linking risk to return created new advanced asset allocation and risk management strategies. For investors, it is now possible to quantify a portfolio’s risk level to develop portfolios at all risk levels to meet investment goals. It has also allowed other investors to expect a higher return if they assume more risk. That simple idea has re-shaped investing.











